Table of Contents |
Electrical safety is critical to modern infrastructure in various settings. Protection from overloads and short circuits is essential. Two primary devices serve this crucial purpose: fuses and circuit breakers. These components offer effective protection for electrical networks. They prevent potential hazards and ensure safe electrical operations.
What Are Fuses and Circuit Breakers?
Fuses are simple devices. They are designed to protect circuits from excessive current. They feature a thin metal wire or strip. It melts when electrical current exceeds a specific threshold. Fuses are commonly used in various settings like household appliances and electrical panels. Automotive electrical systems also use them. When a fault occurs, the wire breaks, interrupting the electrical flow and preventing potential damage.
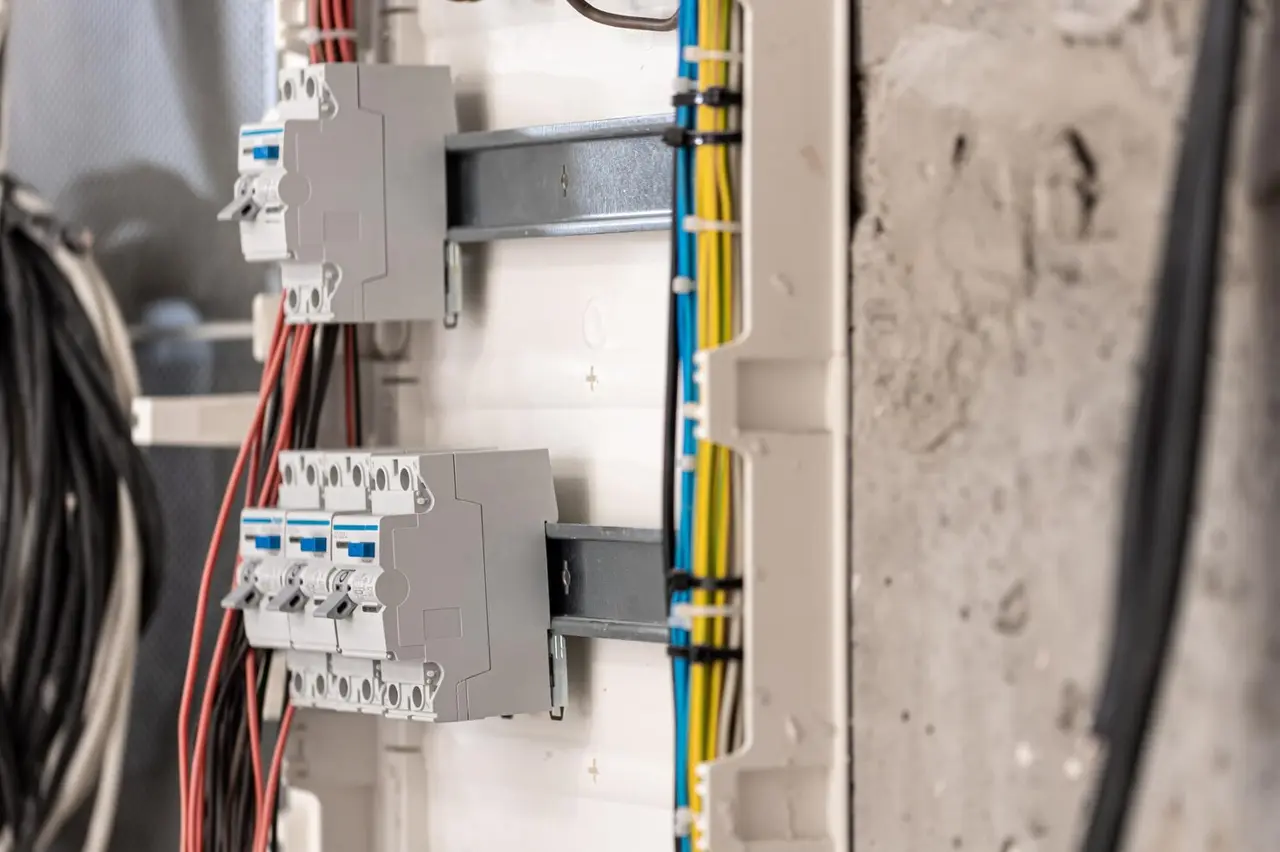
Circuit breakers are more advanced electrical protection devices. They automatically interrupt the electrical flow when overcurrent or short-circuit conditions occur. They come in various types, each suited to specific applications:
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB): These devices are designed for low-current systems in residential and commercial setups. They protect against overloads and short circuits.
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB): These devices are ideal for industrial applications where higher current ratings and adjustable trip settings are needed.
- Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB): These devices provide protection against earth leakage faults, reducing the risk of electric shocks and fire hazard.
- Residual Current Operated Circuit Breaker (RCBO): These devices offer protection against both overcurrent and earth leakage in a single device.
The ability to reset is the main fuse vs circuit breaker difference. You can reset a circuit breaker after it trips. They provide comprehensive protection and the ability to quickly restore electrical connections.
Pros and Cons of Fuses
Fuses, like any technology, come with their own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding their pros and cons helps with fuse vs circuit breaker decision-making.
Pros
- Low Cost: Fuses are generally cheaper than circuit breakers. Ideal for budget-conscious installations.
- Fast Response Time: They react quickly to electrical faults and provide immediate protection against overloads.
- Simple Design with No Moving Parts: This is a key difference between circuit breaker and fuse. No moving parts of fuses mean fewer potential mechanical failures.
Cons
- Need Replacement After Every Fault: This is a primary fuse vs circuit breaker difference and a major fuse con. You need to replace it every time it blows.
- Not Reusable: A fuse is a single-use protection device. Hence, you may need to have a constant stock of spare fuses.
- Limited Protection: Fuses are less effective in complex electrical systems. They are not designed to handle sophisticated power requirements.
Pros and Cons of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are a more modern electrical protection approach. The fuse vs circuit breaker comparison highlights how their design reflects the evolving need for electrical safety.
Pros
- Reusable After Tripping: This is a primary fuse vs circuit breaker difference and a major pro of using circuit breakers. They can be easily reset without replacement and offer immediate restoration of power.
- Easier Maintenance: Circuit breakers are simple to operate and manage. This reduces technical complexity.
- Advanced Safety Features: Options like Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter AFCI are available to provide comprehensive electrical protection.
Cons
- Higher Upfront Cost: Cost is another major fuse vs circuit breaker difference. Circuit breakers are more expensive than traditional fuses. The initial investment is substantial.
- Slightly Slower Response Time: They are marginally less rapid than fuses. Their slower response time translates to a microsecond difference in fault detection.
- Requires Periodic Maintenance: Circuit breakers require regular testing and potential calibration. This key difference between circuit breaker and fuse may add to long-term operational costs.
Which is Best for Your Needs?
The fuse vs circuit breaker selection depends on specific requirements and environment. Understanding your electrical setup helps make the most suitable selection.
For Homeowners
Modern residential settings typically prioritize cost and convenience. Cost is a key difference between circuit breaker and fuse. While fuses are relatively cheaper upfront, circuit breakers offer better long-term value despite higher initial costs. Their ability to be reset and additional safety features make them more attractive. They are also suitable for homeowners seeking solutions that provide peace of mind.
Safety is also a top priority for homeowners. They benefit from circuit breakers’ advanced protection, especially with GFCI options that protect against ground faults. The convenience of simply flipping a switch after a trip outweighs the cost difference.
For Industrial and Commercial Use
Complex electrical systems demand reliable protection and safety. Circuit breakers provide more comprehensive safety mechanisms for complex networks. Large-scale industrial environments require sophisticated electrical management strategies. These settings often involve high-power equipment and precise electrical control requirements.
Industrial environments require consistent performance and minimal downtime. Circuit breakers’ reusability and advanced protective features make them an ideal choice. They are more suitable for maintaining continuous operations. They help prevent production interruptions and potential financial losses. They also offer more precise monitoring and diagnostic capabilities.
Conclusion
Understanding the fuse vs circuit breaker differences is crucial for effective electrical safety. While both serve protective functions, they differ significantly in design, cost, reusability, and application complexity. Overall, circuit breakers offer more versatility and advanced features, making them a preferred choice in various settings.
At CHINT, we provide reliable electrical protection solutions. Our product range includes robust options like the 9FP Fuse Set, NB1-63H Miniature Circuit Breaker, and NB2LE-40ZT Smart Residual Current Operated Circuit Breaker. Visit our website to browse our full product catalog.







-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)






