Table of Contents |
When it comes to power regulation, transformers are everything. Step-up and step-down transformers can boost or lower voltages to apply whatever level of power is necessary for a given application, and as long as transformer noise isn’t part of the electrical system, they’ll do their job reliably and effectively.
But transformer noise can be a significant problem. Even small amounts can gum up the works and prevent power transformers from working the way they’re designed, should so it’s important to know exactly what transformer noise is, what’s causing it, and how to prevent it.
What follows is a review of those three elements of transformer performance, along with some appropriate recommendations and a review of two of the best transformer products in the industry.
What Causes the Humming Noise in an Electrical Transformer?
One of the most common symptoms of excessive transformer noise is that familiar humming noise that transformers emit. But determining whether the amount of noise is excessive is trickier than it sounds.
Why? Because all transformers “hum” to some extent due to the flow of alternating current through the transformer, which has a magnetic effect on the iron core of these devices.
A certain amount of humming is normal, but there are steps to control it if the transformer’s performance measurements are outside the specified parameters for current, voltage or both. It can also be necessary to do this in certain work situations as well to keep workers more effective and productive.
Let’s look at a few of the tactics you can use to reduce or eliminate audible humming, starting with some steps you can take during installation and mounting.
How Can You Stop Transformer Noise from Happening?
Select a Low-Traffic Installation Site
The first step in reducing transformer noise is to select a proper low-traffic site. In this case, “traffic” refers to both the movement of people and the presence of other electrical devices. Either can cause excessive humming, but other devices are far more likely to be the culprit, especially in office spaces where computers and other electronics are present.
Avoid Corners, Stairwells and Corridors
The next step has to do with spacing. Specifically, putting transformers in tight spaces amplifies the noise and humming, and it also reflects back any interference that may be present. To counter this, make sure your transformers aren’t located in corners, corridors or stairwells whenever possible.
Mount the Unit on a Solid Surface
Also, always mount your transformers on a solid surface. Plywood surfaces amplify noise, and so do thin walls that are basically used as curtains in interior structures. To get ideal performance, transformers work best when mounted on heavy, dense surfaces like concrete floors or walls, so these should be your preferred surfaces whenever possible.
Tighten the Bolts on Enclosures
If you do have to mount them in other places, you can use flexible mounting to reduce metal contact to reduce noise transmission. Wherever you mount your transformers, make sure the bolts and screws on the transformer are adequately tightened. Loose parts will add vibration, which increases the hum, and you should always make sure to avoid lifting eyebolts, as these can also increase noise if used during installation.
Use Acoustical Dampening Material
In addition, there are several proactive steps you can use to reduce the effects of humming on those who have to work in areas where transformers are present.
One is to use acoustic dampening material, which will help keep the noise from spreading. Acoustic tile is one of the best dampening materials you can use, and fiberglass and kimsul are other solid examples of good dampening material.
Another one is to use materials like oil barriers or cushion padding. These won’t eliminate the noise, but they will make it easier for people working in transformer areas to deal with the hum, which can be irritating.
One final note about transformer humming—always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when you install and set up transformers.
These specs tend to be very specific when it comes to issues like the use of dampeners, screws and bolts, and attention to the details contained in the specs is important when it comes to getting the most out of your transformers.
CHINT Power Transformer Solution
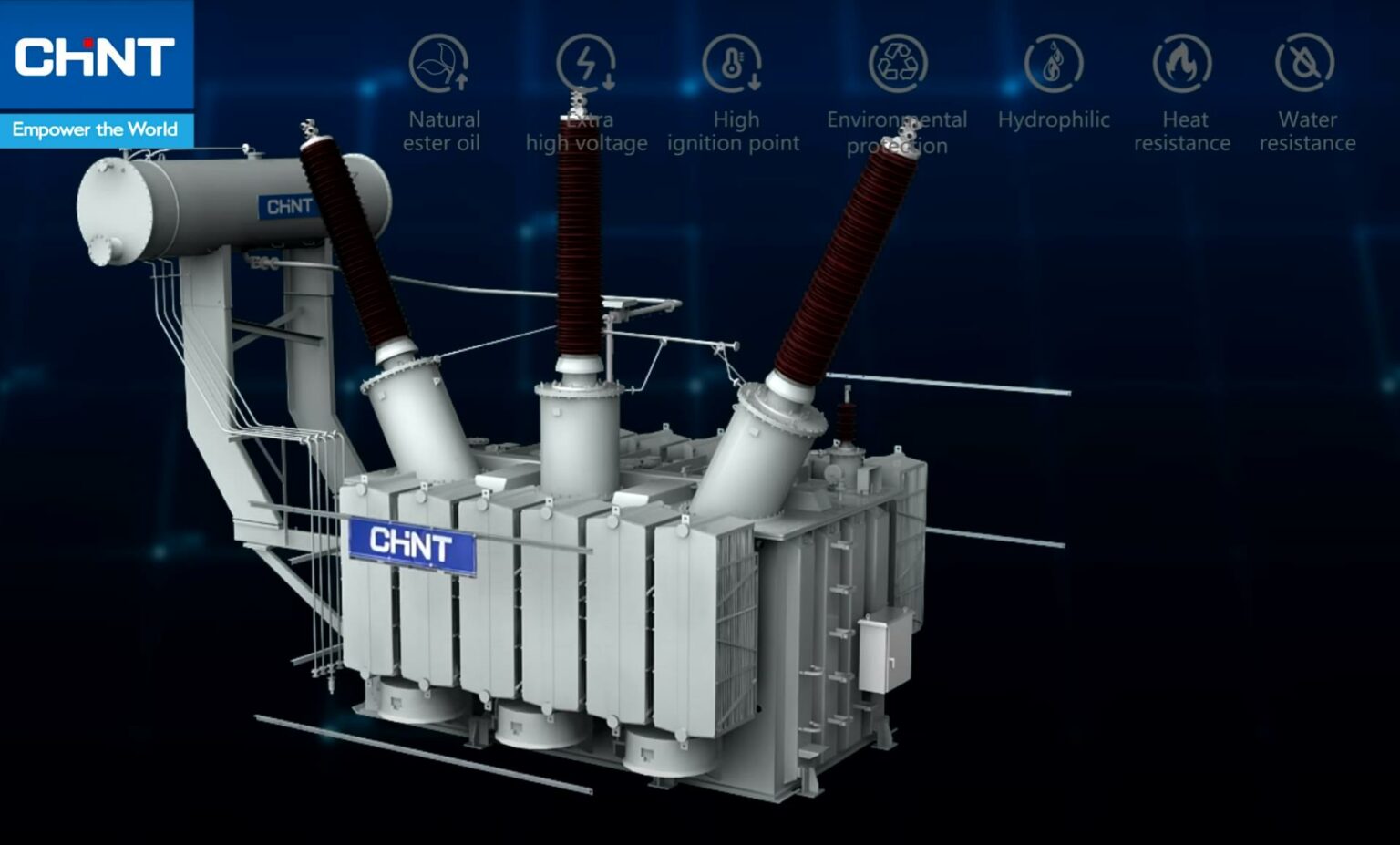
220kV Power Transformer
When it comes to transformer solutions, the 220kV Power Transformer is one example of an excellent solution.
It’s suitable for a number of applications where power is essential, including power plants, substations and large-scale industrial settings.
This transformer conforms to all the necessary specifications, including IEC 60076-1, ANSI, AS, IEEE and other IEC standards. The voltage range is 50/60Hz at 220kV, with a capacity that ranges from 16,000-780,000kVA. These transformers deliver high reliability and performance security, and their efficiency rating is superb.
This transformer also provides extra strength in both insulation and short-circuit protection, along with a a compact, lightweight design and low noise capability. In addition, they can easily be customized and easily delivered with a quick turnaround.
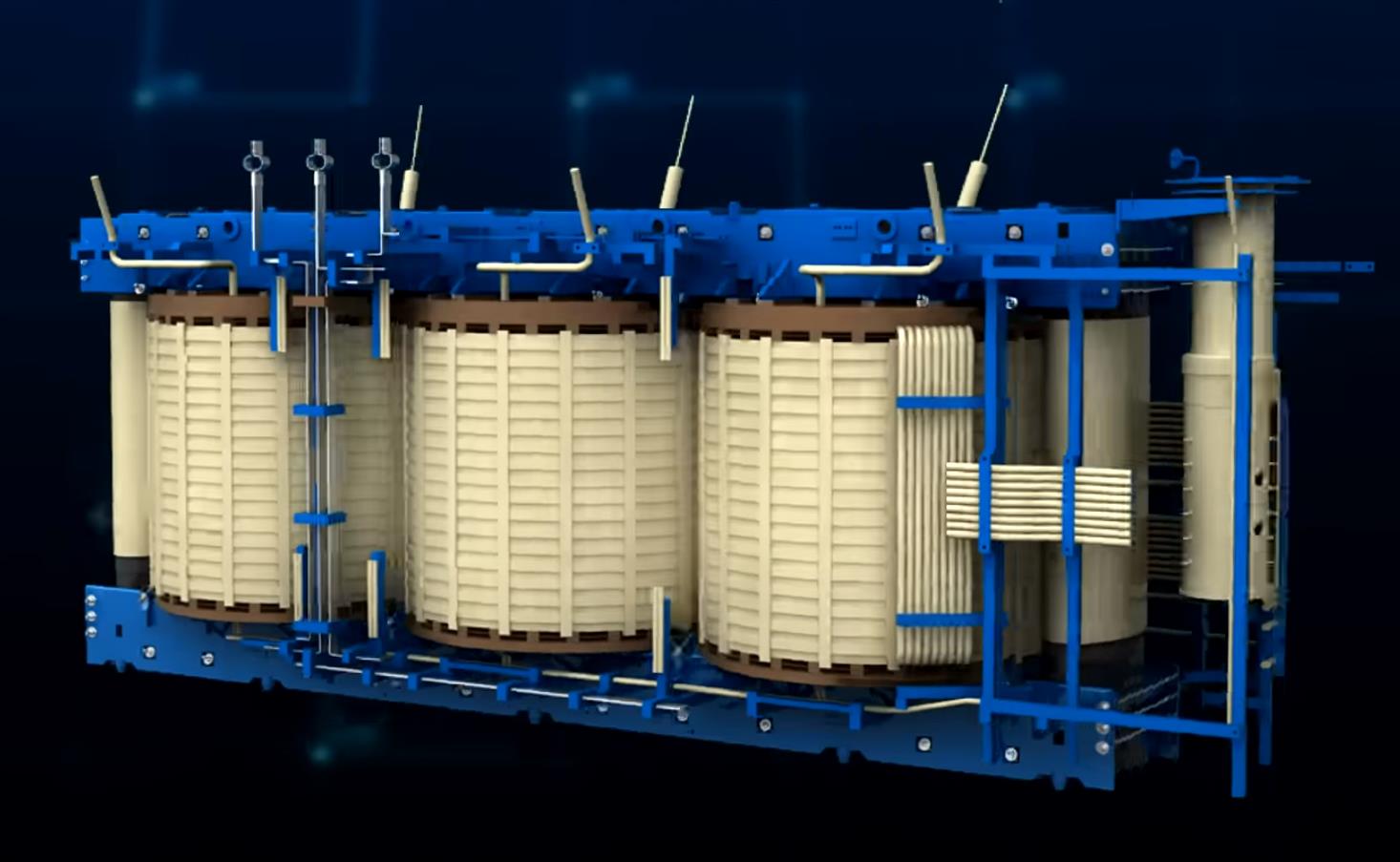
Amorphous Alloy Core Dry-type Transformer
The Amorphous Alloy Core Dry-type Transformer is another excellent choice for applications like high rise buildings, commercial settings, subways, airports, etc.
It also meets the IEC 60076-11 standard, with a rages capacity of 30-2500kVA and an HV voltage rating of 10kV. These power transformers provide analogous high performance, including mechanical strength, excellent thermal stability, and the ability to increase capacity in a small, lightweight package.
Summary
No one fancies the noise produced by transformers. That said, with the tips above you can almost certainly of reduce the noise produced by your transformer and can provide a quieter residential and work environment.









-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)




