| Table of Contents |
Electrical safety is a critical concern, as it involves various risks. One significant hazard in electrical system is short circuit. It can cause severe damage to equipment and pose a threat to human life. Therefore, reliable monitoring and protection devices are needed against it. This article will discuss what short circuit current is, and why protective devices such as RCCBs, MCCBs, and MCBs are essential for ensuring electrical safety.
What is Short-Circuit Current (SCC)?
Electricity has various key traits. One noticeable here is that it always takes the easiest path. So, when wires accidentally touch or connect to the ground, the problem occurs. It’s because they give electricity a shortcut. This can create thousands of amps in less than a second.
It is crucial for electrical system safety and reliability. This knowledge influences several key aspects of electrical design and protection:
- Short-circuit currents determine an equipment’s ability to survive fault conditions. They help to prevent catastrophic failures by identifying component current tolerance limits.
- SCC calculations guide protective device placement and overall electrical system architecture.
- Short circuit current levels directly determine appropriate circuit breaker specifications. They help ensure protective devices can safely interrupt fault currents without system compromise.
How to Calculate Short-Circuit Current
Calculating short circuit current requires considering multiple system parameters. Let’s explore the key methods and factors:
1. Basic Calculation Methods
Accurate short circuit current calculations involve several approaches:
- You can use transformer specifications as primary inputs. Consider capacity(S) and impedance(Z%) to provide baseline fault current values at the transformer secondary. Here is the formula:
- Account for system impedances by considering line resistance(R) and reactance(X). These provide more precise results for calculating short circuit current. Here is the formula:
2. Factors to Consider When Calculating SCC
Several key elements influence calculating short circuit current:
- Power source voltage and impedance significantly determine the maximum available fault current levels.
- Conductor/line material and length impact SCCs, with cable impedance reducing available fault current values.
- Connected loads influence system behavior during faults. Motor contributions potentially increase fault current magnitudes.
The Impact of Short-Circuit Current on Electrical System Design
A proper understanding of short circuit current impacts system design significantly. It influences protection schemes and equipment selection.
1. The Importance of Selecting Proper Protective Devices
Choosing appropriate protection requires careful considerations:
- MCBs and MCCBs must match system requirements, with interrupting capacity exceeding maximum fault currents.
- Equipment short circuit current ratings (Icu, Ics) must align with potential fault currents for reliable protection.
2. Risks Associated with Excessive Short-Circuit Current
High fault currents pose several significant risks:
- Excessive currents can instantly destroy electrical equipment through intense heat and magnetic forces.
- Short circuits create dangerous arc flash hazards. They pose severe risks to personnel safety.
- Fault-related damage causes significant operational interruptions and potential system downtime.
3. How to Mitigate High Short-Circuit Currents
Several strategies help manage high short circuit current levels:
- Current-limiting circuit breakers reduce peak fault currents for better equipment protection.
- Strategic impedance placement (increasing where necessary) helps control fault current levels.
- Selective coordination ensures proper protection sequence, minimizing fault impacts.
The Role of RCCBs in Electrical Protection
These devices protect against electrical leakage currents in modern installations. They are distinct from short-circuit protection devices. However, their role is vital for personnel safety and fire prevention. The key highlights include:
- RCCBs constantly monitor the current flow between phase and neutral. They disconnect power when dangerous leakage occurs.
- They work best when paired with MCBs/MCCBs for comprehensive circuit protection.
- These devices require specific ratings and breaking capacity based on application environment, to ensure reliable protection.
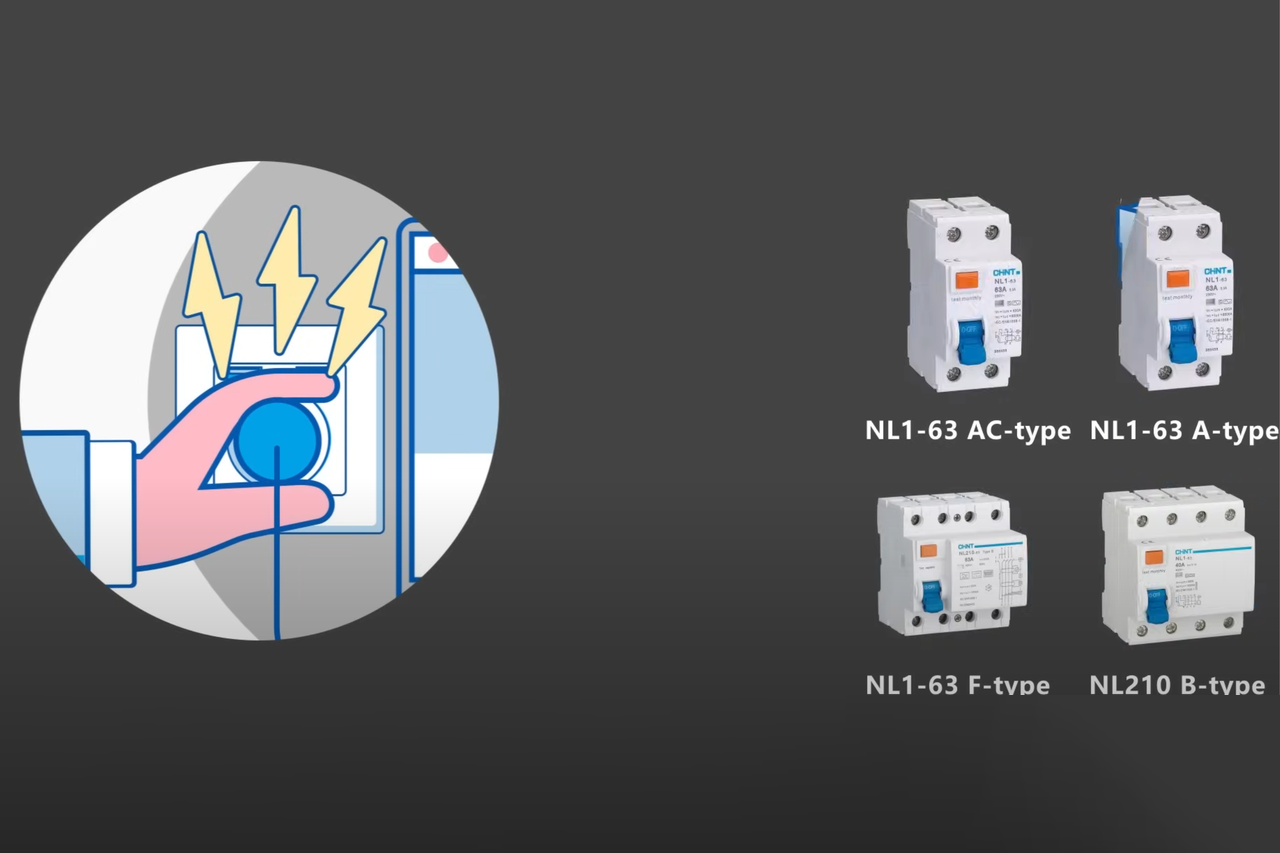
Recommended Product: CHINT NL1 Series RCCB
At CHINT, we understand these critical protection needs. Our NL1 Series RCCB represents advanced safety technology. This versatile device provides reliable protection against leakage currents while ensuring operational stability across various applications.
1. Features of CHINT NL1 RCCB
Our NL1 Series combines innovative technology with practical functionality to deliver superior leakage current protection. Its key features include:
- Offers precise detection of AC and pulsed DC residual currents with class A and AC options. It ensures reliable tripping across various current waveforms.
- Provides complete circuit protection when integrated with MCBs/MCCBs. It boasts surge protection up to 3000A and prevents nuisance tripping.
- Built with high-durability design. The NL1 RCCB maintains stable performance in demanding conditions. It ensures consistent operation under surge impacts.
2. Typical Applications
The NL1 Series adapts to various protection requirements across different sectors:
- It delivers reliable protection in residential and commercial buildings. The RCCB protects against electrical leakage hazards and indirect contact.
- The device provides robust protection for industrial machinery. It features adaptable sensitivity options for different industrial environments.
- The NL1 Series seamlessly combines with other protective devices (e.g. circuit breakers). In this way, it creates comprehensive electrical safety systems hence enhancing overall protection reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding SCC and proper protection is crucial for electrical safety. Selecting appropriate protective devices is important crucial. These include MCB, MCCB, and RCCB. They ensure system reliability and personnel safety. Visit CHINT website to explore more product range and ensure your electrical system’s safety.