Table of Contents |
Industrial and commercial distribution systems use several methods to transport electrical energy. The most common examples of these methods include heavy conductors running in trays or conduits. Cable and conduit are often inflexible once installed. However, a more flexible and preferred option is to use a busway, also known as bus ducts, which are essentially bus bars in busway exposure.
Below is everything you need to know about busway and busway exposure, including the different busway components.
What Is Busway and Busway Exposure?
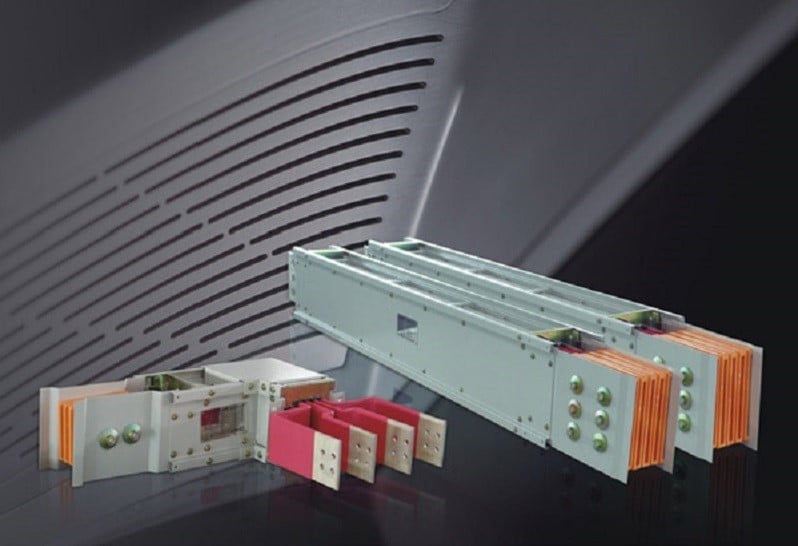
According to the National Electrical Manufacturer Association (NEMA) , busway is a prefabricated electrical distribution system that consists of bus bars in a protective enclosure (busway enclosure), including straight lengths, devices, fittings, and accessories.
This system transports electricity and connects to electrical gear like panelboards, switchgear, and transformers. A busway enclosure comprises bus bars, a housing, and support and/or insulating material.
Busway and cable and conduit are often compared for several reasons. However, they both provide the same function, which is to deliver power between electrical equipment. The major difference is that busway uses less material since each piece is designed for a specific job and comes with a small cross-sectional area.
In addition, it has a lower voltage drop compared to cable and conduit because of the solid phase bars. This results in lower impedance. Moreover, the installation of busway is typically less labor-intensive than the installation of cable and conduit.
Types of Busway (Bus Ducts)
The main types of bust ducts include:
Non-segregated Busway
These bus ducts have copper phase bars situated in an enclosure separated by air and epoxy insulation. The enclosure or housing materials tend to vary from steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Its environmental ratings include outdoor, indoor, and dust tight. Non-segregated phase busway can provide both medium and low voltage solutions and is well suited for harsh environments.
A non-segregated busway is used in applications up to 38kV and 6000A. You will find it mostly in electrical utilities, heavy industry, and petrochemical sites.
Sandwich-Style Busway
These bus ducts have phase bars stacked together inside a non-ventilated steel or aluminum enclosure. You can use a sandwich-style busway to deliver power between gear with feeder pieces.
A plug-in busway, which is typically a busway with tap-off locations placed on it, is used to power equipment below the busway. Generally, a sandwich-style busway is a cost-efficient solution in different sectors since it can provide high ampacity with high short-circuit withstand ratings.
It is utilized in applications up to 600V and up to 5000A. Common applications for a sandwich-style busway include data centers, commercial construction, and general heavy industry.
Track Busway
The bus duct is a continuous rail design where tap-off boxes can be removed or installed almost anywhere along the bus ducts system. These boxes have fixed receptacles and cord whips that allow for distributing power to equipment under the busway.
It is mostly found in data center markets but is also practical in labs and warehouse applications. It is available up to 1000A and 600V and is rated for indoor use.
Air-Insulated Busway
These bus ducts feature either aluminum or copper phase bars held in place with polymer support in an aluminum enclosure. It has plastic clips that keep the conductors isolated and spaced, guaranteeing air circulation.
The air-insulated bust ducts are indoor rated and feature plug-in as well as feeder designs. The air-insulated busway can provide medium ampacity and low voltage solutions with robust safety ratings. In addition, it is available up to 600A and 600V. It is commonly used in labs, machine shops, and data centers.
Busway Used in A Distribution System
Busway, also referred to as bus ducts, functions just like cable and conduit assemblies. One of busway’s major pros is how easily its sections are linked together. Connecting standard busway lengths can supply electrical power to any area of a building. Generally, installing or changing a busway system takes much less time than cable and conduit systems. However, in some instances, a complete distribution system comprises a combination of busway and cable and conduit.
Busway commonly has varying applications. You can find it in industrial installations and high-rise buildings. It is mostly used in industrial locations where they supply power to heavy equipment, air conditioning, and lighting.
Expect to find bus ducts in industrial facilities, electrical utilities, petrochemical utilities, large residential complexes, data centers, and mission-critical facilities.
Busway Components
Busway comprises several components. These include:
Bus bars
These are essentially conductors that conduct electricity. Bus bars vary in size and are made from copper or aluminum. A bus bar is represented schematically by a straight line with several connections made to it. Bus bars are generally uninsulated and feature adequate stiffness to be supported in the air by insulated pillars.
Housing
The busway enclosure is designed to contain the bus bars. It is made from steel or aluminum.
Insulating system
The system separates the bus bars from each other to hinder electrical faults. The insulating system is made of a combination of epoxy, air, and mylar.
Fittings
These include offsets, elbows, and tees that assist in properly routing bus ducts from one electrical connection or termination.
Summary
In a nutshell, bus ducts are prefabricated distribution systems consisting of bus bars in busway enclosures. There are different types of busway, including non-segregated busway, track busway, air-insulated busway, and sandwich-style busway. The different components of busway include bus bars, fittings, housing, and insulated systems.
One of the most common examples is the HV&LV Busway from CHINT. CHINT is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality electrical components, devices, and accessories used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Consult an expert electrician to advise you further on busway examples and applications.










-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)




