Table of Contents |
Electrical power grid failures can have devastating effects on data center equipment, IT hardware, and office systems due to electrical surges. In addition, the loss of data, employee downtime, and supply chain disruptions all contribute to the cost of not having power when your business needs it.
Power distribution units (PDUs) distribute power and protect IT loads running normally. Conversely, uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs) ensure there is enough power, at least for a short time, to run your equipment until you can find another available power supply (i.e., a backup generator).
While both devices protect your crucial systems, there are differences between PDUs and UPSs. To ensure proper power management and protection of your data and equipment, it’s vital to know what the differences are and how to choose the right option for your data center.
What is a PDU?
A power distribution unit (PDU) is an electrical device that monitors and distributes power to multiple outlets within a data center. Since rooms with multiple computers draw more power than typical home applications, PDUs are indispensable for even power distribution to all your computer and information system hardware.
Basic PDUs, as the name implies, serve the primary function of power distribution, whereas metered input PDUs are more intelligent and have built-in meters to monitor load output. The data can then be used to determine power usage effectiveness.
The next step up in power distribution devices is switched PDUs. These units have the same monitoring capabilities as metered PDUs but also allow you to switch individual outlets off or on remotely. The main advantage of this type of PDU is that it increases safety, protects equipment, and reduces energy costs.
What is a UPS?
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) provides emergency power to a load during a power outage. Unlike an external generator, a UPS kicks on automatically to provide instantaneous power, usually through the use of batteries or supercapacitors. There are three main types of UPS:
Standby UPS Systems
Standby UPS Systems have a switching function that automatically turns on an alternate power source, such as a generator, during power outages. They typically also have features such as surge protection and remote monitoring.
Inline Interactive UPS Units
Inline Interactive UPS Units monitor incoming voltage and automatically regulate abnormal readings. If the voltage falls outside normal parameters, the UPS will use built-in transformers to either raise or lower the voltage to bring it within the normal range.
Double-conversion UPS Modules
Double-conversion UPS Modules convert anomalous utility voltage to DC power. Then, an inverter converts it into filtered AC power to protect against power surges, sags, swells, and line drops.
PDU vs. UPS: Key Differences
Even though there are similarities between the two components, they each serve a different function from each other. For example, PDUs distribute power to your equipment, whereas the purpose of a UPS is to provide backup power using batteries stored in the server rack.
PDUs make use of several connection points to distribute power to IT hardware within a data center. UPS systems, in contrast, provide battery backup in case of a power outage. While each component serves a different purpose, both help protect your equipment from damage due to power surges and voltage spikes.
Choosing the Right Solution: UPS vs PDU
When choosing between a UPS and PDU, the power requirements of your equipment are the most crucial variable.
For example, hospitals, clinics, and government offices rely on uninterrupted power 24 hours a day, and any disruption could be catastrophic. In these environments where power outages could mean the difference between life and death, you need a UPS to provide the power to run critical systems.
On the other hand, if you simply want even power distribution across IT hardware in your data center, a PDU will suffice. Also, if cost is a factor, you can save money by opting only for a PDU.
For some important applications, such as data centers, medical care, finance, and the Internet, UPS+PDU solutions is the best and highly-recommended option.
Combining PDU and UPS for Comprehensive Power Management
What if you could combine a UPS’s reliability with the safety and versatility of a PDU? These devices would work together to ensure reliable power backup, distribution, and protection for critical systems.
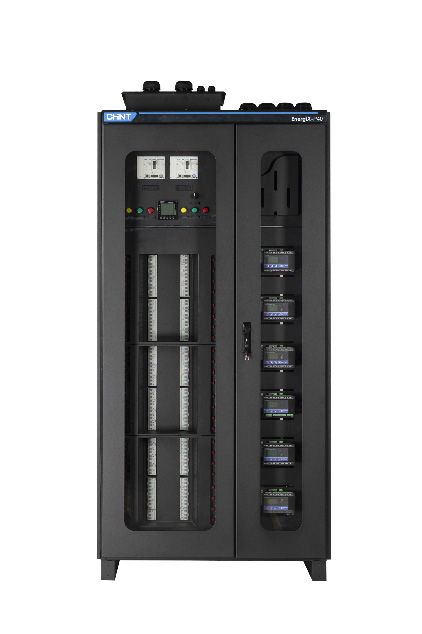
Chint Global’s EnergiX-P40 Low-voltage Power Distribution Unit does all that and more by combining the reliability of a UPS with the protection and distribution of a PDU. In addition, the EnergiX-P40 provides a live-swappable modular layout that is flexible yet functional and offers high capacity, intelligent monitoring, and remote management.
Conclusion
When thinking about PDU vs UPS, the differences are apparent: A UPS provides backup power to critical data systems during a power outage, whereas a PDU distributes power to various IT hardware. You should have an idea by now of what they are so you can make informed decisions concerning power distribution within your data center or office.
The Chint EnergiX-P40 Power Distribution Unit (PDU) provides maximum protection against power outages and overcurrents resulting in damaged equipment. It features a modular layout, live-swappable circuits, and an intelligent monitoring system for remote data management, security, and maintenance. To find out more, visit our product page at chintglobal.com.










-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)




