Table of Contents |
Circuit breakers are essential safety electrical devices. RCBO and RCCB are two common types of circuit breakers that monitor the current flow and provide protection for devices, circuits, and human bodies. However, the differences between them remain obscure to many. Therefore, this guide will clarify the differences between RCBO and RCCB so that you can pick the right one for your needs.
What is a Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)?
A residual current circuit breaker is a safety electrical device that detects and breaks the electrical circuit in the event of a leakage current. It interrupts the circuit to protect devices from fire and people from electric shocks.
Working Principle of RCCB
The working principle of RCCB is based on Kirchhoff’s current law. This law states that the sum of currents entering the node should be equal to the sum of currents exiting the node. In normal conditions, the current flowing through the live and neutral wires should be equal and opposite.
However, there will be an imbalance between the live and neutral currents (called residual currents) when there is a fault. For example, when a human touches a live wire, some current will flow to the ground via an alternative path. This deviation is what a residual current circuit breaker detects and instantly trips the circuit in milliseconds.
Main Function of RCCB
The main function of RCCB is to provide earth fault protection. It continuously monitors the difference in current values between the live and neutral wires. When the residual current due to any fault exceeds the limits, it interrupts the circuit. This way, it protects from electric shock and other hazards.
Types of RCCB
RCCB comes in different types based on design features and specific capabilities. Mostly, the types of RCCB are divided based on the number of poles (2 pole and 4 pole) and tripping curve characteristics (AC, A, B, and F). Below is a quick glimpse of all types of residual current circuit breakers:
- 2 Pole: It is used for single-phase circuits and connects one live wire and one neutral wire.
- 4 Pole: It is used for three-phase circuits and connects three live wires and one neutral wire.
- Type AC: It responds to only alternating currents (AC).
- Type A: It responds to both AC and pulsating direct currents (DC).
- Type F: It responds to AC, high-frequency AC, and pulsating DC.
- Type B: It responds to AC, high-frequency AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC currents.
The above types of RCCB breakers are used in different types of applications, such as residential, commercial, etc.
What is a Residual Current-operated Circuit Breaker (RCBO)?
RCBO refers to residual current-operated circuit breakers or residual current circuit breakers with overcurrent protection. In the context of RCBO vs RCCB, an RCBO provides added protection from overload and short circuits.
Working Principle of RCBO
The working principle of an RCBO against earth leakage is also based on Kirchhoff’s principle, i.e., the incoming and outgoing currents should be equal. So, an RCBO also monitors the difference in current values between live and neutral wires and breaks the circuit if a mismatch exceeds the safety threshold.
Similar to regular MCBs, the working principle of an RCBO against overcurrent is generally based on electromagnetic induction and the invention of bimetallic strips. In the case of short circuits, the electromagnetic trip coil in the RCBO swiftly responds to the induction and trips the circuit breaker. When the circuit is overloaded with electrical devices, the bimetallic strip deflects and trips the breaker.
Main Functions of RCBO
As evident from the working principle, there are three main functions of RCBO:
- Protection from earth fault currents
- Protection from overcurrent due to overloading
- Protection from short circuit currents
In short, RCBO is an all-in-one device to protect domestic and industrial electric circuitry from a variety of electrical faults/hazards.
RCBO vs RCCB: Key Differences
Looking at the above basics of RCBO vs RCCB, it is evident that RCBOs offer more protective functions than RCCB. RCBO protects from earth faults and overcurrent. In contrast, RCCB protects from earth faults only.
Furthermore, an RCBO generally has a higher initial cost compared to an RCCB. That’s why many people tend to connect the RCCB to an MCB for the same protection as an RCBO provides.
Conclusion
RCBO and RCCB are two popular circuit breakers used in wide applications. As evident from the above thorough RCBO vs RCCB comparison, an RCBO provides protection from earth fault (residual current) and overcurrent while an RCCB protects from earth leakage only. However, the selection of circuit breakers should not be simply based on functionality, but on budget, existing systems, etc.
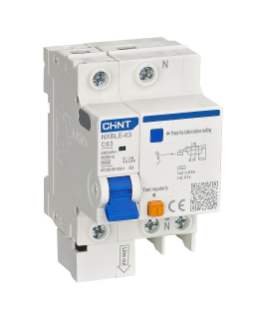
To get the best quality circuit breaker, CHINT is the leading brand to consider. CHINT NXBLE series residual current operated circuit breaker (RCBO) offers various types and capacities of RCBOs with long-lasting reliability. Browse CHINT RCBO products and pick the ones that match your circuit needs.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to us.











-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)






