In recent years, the global PV industry is making leaps and bounds, and the PV market is still growing at a high rate despite high silicon prices and freight costs pushing up the cost outlay for PV projects. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) data, although the growth rate of global cumulative installed capacity has slowed, sustainability has significantly strengthened.
China, the United States, and India as the giants of the cumulative installed capacity, the growth of the overseas market has driven the domestic market. Currently, the scale of new PV installations in China is exceeding expectations, and silicon and module manufacturers are expanding significantly due to strengthening global demand.
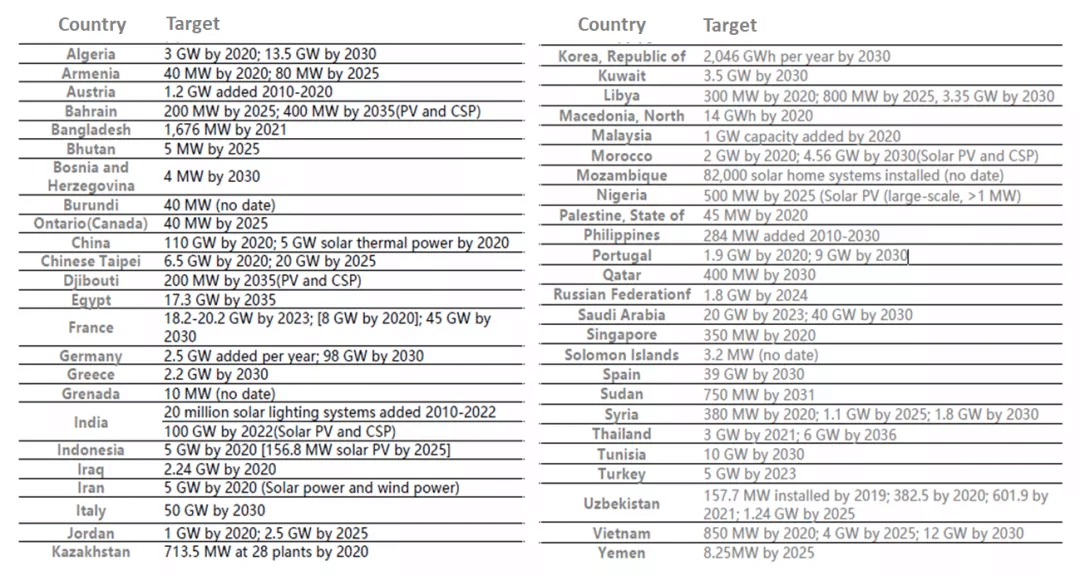
To combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, several countries around the world have set development targets for installed PV capacity by 2030, seeking to accelerate the energy transition and achieve the countries’ carbon neutral commitment targets.
European Markets Drive Growth
While the United States and China are investing the largest share of the renewable energy market, some countries in Europe, too, are pushing the PV industry forward. The European Commission has set a new binding renewable energy target of 38-40% for 2030, while the European Parliament on October 6, 2020, increased greenhouse gas emissions (compared to 1990) from the current 40% reduction target to 60% for 2030.
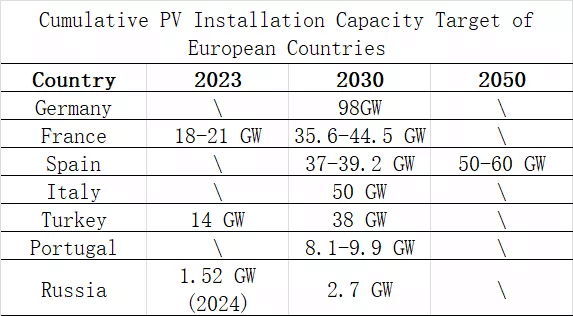
Renewable energy targets are also implemented in the PV sector, with important European countries (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Turkey, Russia) setting cumulative PV installation targets for 2030 totaling 254.3 GW.
Significant Growth Forecast in the Asia-Pacific Region
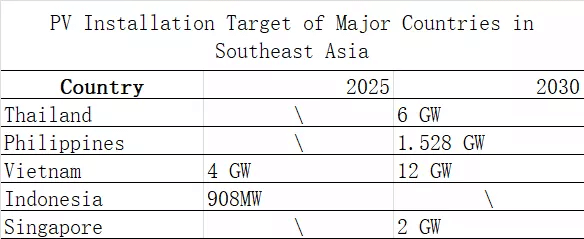
In order to stimulate the recovery of the domestic market, ASEAN plans to reach 23% of the overall energy supply from renewable energy by 2025. In the 2025 energy planning blueprint, the maximum installation of photovoltaic will reach 55 GW, following this logic, the ASEAN countries need to reach 7.26 GW of photovoltaic installation each year from 2018.
For the United States: The Solar Energy Association of America (SEIA) has proposed a goal of 20% of national electricity generation from solar power by 2030. In order to achieve this goal, the United States needs to install a cumulative 500 GW of solar projects by 2030. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is expected to reach 46% of the total installed PV capacity in renewable energy by 2050, with an installed capacity of 920 GW.
On the other hand, the U.S. Department of Energy also attaches great importance to the sustainability of the PV industry and in 2019 proposed the Sunshot 2030 program, which aims to further significantly cut the cost of kilowatt-hour electricity by:
- $0.05/kWh for residential PV
- $0.04/kWh for commercial PV
- $0.03/kWh for utility PV
India: India’s Ministry of Energy (MNRE) had proposed in 2015 to reach 100 GW of installed solar power in India by 2022. The main elements of the target include the realization of 40 GW of rooftop power plants while building 60 GW of ground-mounted power plants. By the end of 2019, India’s cumulative installed PV capacity of 42.8 GW.
The development of the global PV industry is defying the epidemic and achieving counter-trend growth, with the manufacturing side continuing to expand and global polysilicon production achieving year-on-year growth. Chinese photovoltaic enterprises with the advantages of technology and cost control, production capacity as well as the manufacturing end of the production capacity is growing, the global PV industry is also further to China over.
With the rapid development of photovoltaic technology and global energy strategy transformation, the global installed demand for PV will have dozens of times more space in the next two decades.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the cumulative global installed capacity of PV will reach 2,400GW in 2035, and the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) expects that the cumulative global installed capacity of PV will reach 8,519 GW in 2050. If PV can meet 25% of electricity demand in 2050, the total global installed capacity can reach 8.5 TW. In the sustainable development scenario, the future under sustainable development scenario, the PV industry will lead in the annual electricity generation.