Table of Contents |
Dry-type transformer vs. oil-filled transformer is the most common debate in the market today. If you, too, are confused about whether to go for dry-type transformers or oil-filled transformers, then read this article till the end!
This post is the ultimate guide for people confused about how they differ from each other.
Transformers are becoming increasingly popular for altering the voltage in conventional power circuits. Whether you want to reduce the voltage to operate low-powered devices or raise the voltage to allow for long-distance electric power transmission, transformers are the way to go!
There are two types of transformers: dry-type transformers and oil-filled transformers. Even though they have the same objective, these transformers differ significantly. These distinctions are significant enough that the different transformer types are better suited to specific applications.
This article highlights the differences between dry-type transformers and oil-filled transformers. You will distinguish between their cost, maintenance, noise, energy efficiency, etc. So, let’s get started, shall we!
What is a Dry-Type Transformer?
A dry-type transformer is a motionless piece of equipment that uses environmentally acceptable temperature insulation systems. They are also known as “cast resin type transformers.”
The transformer is housed in a case with adequate ventilation, which results in the coils being cooled by the air inside the case. Additionally, they include varnished copper or aluminum windings. Because of the cooling constraints, dry-type transformers’ maximum voltage is restricted to 35kV.
Types of Dry-Type Transformers
The global market for dry-type transformers is estimated to increase at a CAGR of 6.1 percent from 2020 to 2027 due to increasing advancements in the types of dry-type transformers. There are several different types of dry-type transformers on the market, including:
- Vacuum Pressure Impregnated (VPI) Transformers
- Vacuum Pressure Encapsulated (VPE) Transformers
- Open Wound Transformers
- Cast Coil Transformers
Dry-type transformers have a wide range of commercial, industrial, and utility applications. They are commonly utilized in small and medium-voltage applications in electric equipment.
What is an Oil-Filled Transformer?
Oil-filled or oil-immersed transformers are voltage conversion devices that use oil to keep the transformer cool. This type of transformer structure is mounted in a welded steel oil tank filled with oil.
When an oil-immersed transformer is in use, the heat generated by the coil and iron core is first transferred to the insulating oil, then to the cooling fluid. Due to the liquid’s inflammability, oil-filled transformers are mostly used in outdoor installations.
Types of Oil-Filled Transformers
The oil-filled transformer industry exceeded $28.3 billion in 2020. The market is expected to grow at about 3.5% between 2021 and 2027. There are two main types of oil-filled transformers:
- 1-Phase Transformers
- 3-Phase Transformers
Oil-type transformers can be put on the ground, on a pad, or on a pole. They function well in various environments, including transmission and distribution lines, renewable energy generation, and small businesses.
Dry-Type Transformers vs. Oil-Filled Transformers: Key Differences
Take a look at the differences between dry-type and oil-filled transformers to understand how they perform.
1- Cooling Medium
Transformers overheat under load. They need a cooling medium to prevent overheating and potentially causing a fire or explosion.
The most significant distinction between the two transformers is their cooling medium. Dry-type transformers employ air as a cooling medium, while oil-filled ones, as the name suggests, use oil.
2- Maintenance
Oil-filled transformers are more high maintenance than dry-type ones. Oil-filled transformers require additional attention because the oil must be tested for chemical contamination regularly. Additionally, they require oil filtration at least once a year.
Dry-Type Transformers, on the other hand, are chemically resistant. Even if a minor event occurs, they do not need to be disconnected from the grid.
3- Operational Cost
You might assume that oil-filled transformers entail higher costs than the dry types. However, the reality is the contrary.
Oil-filled transformers are less expensive because they use conventional energy efficiency, making them dependable and long-lasting. Dry transformers use more energy and entail a higher operational cost.
4- Recyclability
Dry-type transformers have a restricted coil recycling at the end of their service life, whereas oil units have a much easier core recycling.
5- Efficiency
Oil-filled transformers are more efficient than dry-type transformers, which are larger and have a lower voltage rating. Thus, the dry types are more prone to overheating during overload, resulting in higher electrical losses and maintenance costs.
6- Location
This is arguably the most significant consideration when choosing a transformer and a major difference between the two. Oil-filled transformers are typically installed outdoors due to the risk of an oil spill, which could pose a serious threat.
Dry-type transformers are specifically utilized in buildings since they are less hazardous and safer for the environment. They’re also less explosive, so they’re utilized in malls, offices, hospitals, etc.
CHINT Dry-Type and Oil-Filled Transformer
Although these distinctions are widely regarded as general guidelines, there is always room for exceptions. Many of the world’s largest transformer manufacturers, like CHINT Global, are making significant technological advancements.
If you are confused about which brand to go for, take a look at these best-selling CHINT dry-type and oil-filled transformers:
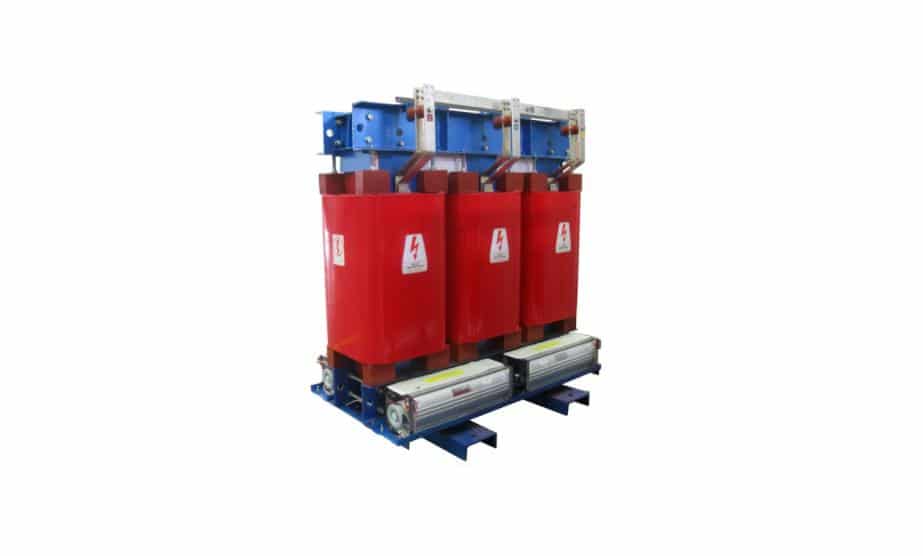
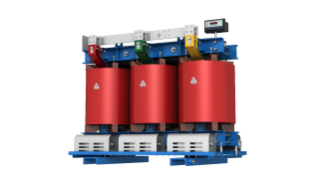
Amorphous Alloy Core Dry-Type Transformer
This dry-type transformer is formed of amorphous alloy ribbon, an innovative type of energy-saving semiconductor. The ribbon comprises iron, silicon, boron, carbon, and other compounds.
Amorphous alloy core provides high saturation magnetic induction, high resistivity, minimal loss, and other advantages over standard magnetic materials.
The CHINT amorphous alloy core dry-type transformer is good for volatile and explosive environments. It is ideal for high-rise buildings, shopping plazas, airports, subways, railway stations, and industrial sectors.
Features:
- Lower operating noise
- Short-circuit resistant
- Excellent thermal performance
- Excellent moisture, fire, and explosive resistance
- Compact and lightweight
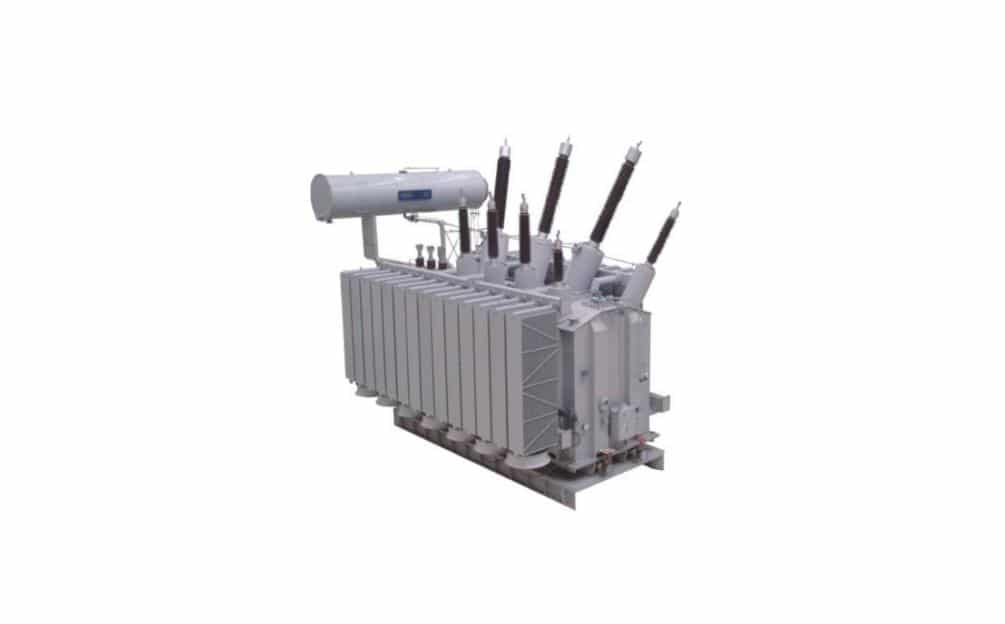
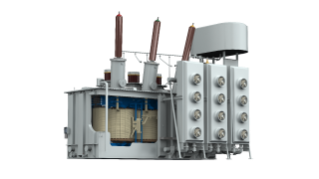
220kV Power Transformer
The CHINT 220kV Power Transformer has a large capacity. Thus, it will save a significant amount of electrical energy, prevent power loss, conserve energy sources, and lower user expenses.
It features a magnetic core, windings, and brushings. Their coils and core are submerged in oil, cooling and insulating them. Convection transports oil via ducts in the coils and around the core assembly.
The CHINT 220Kv Power Transformer is ideal for power plants, power stations, and large-scale industrial applications.
Features:
- High operational security and dependability
- Cost-effective
- Great insulation capabilities
- Compact and lightweight
- Low noise generation
- Fast delivery
Final Wordings
Based on our dry-type transformer vs. oil-filled transformer analysis, oil-filled transformers appear to be a better alternative in terms of energy-saving, cost-saving, and recyclability. Dry-type transformers, on the other hand, are safer for interior operations.
Whether you’re looking for an oil-filled or dry-type transformer, you should always deal with a trusted provider that offers the finest items on the market CHINT dry-type transformers, and oil-filled transformers are the finest choice in this case. With CHINT, you are sure to receive top-quality equipment at reasonable rates!
If you have any questions or need further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to us.


















-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)