Table of Contents |
What is a Distribution Transformer?
A Distribution Transformer is a device that transfers power from the electrical grid to your home, businesses, and commercial buildings. They are often found on poles in residential areas or on the side of buildings where there is a lot of foot traffic. They can also be seen underground in some locations with little room for overhead lines.
These devices are also called step-down transformers because they reduce voltages from higher to lower levels that consumers can handle without damaging their appliances or electronics. Distribution transformers use large coils of copper wire wrapped around an iron core inside the transformer casing. The coils carry the electrical current through the iron core, which transfers energy from one coil to another without breaking down the voltage.
And they’re also different from distribution feeder lines because they only connect to one building or set of buildings instead of combining multiple facilities as feeder lines do.
So, distribution transformers reduce the voltage from a transmission line. And a distribution transformer has the same basic structure as an autotransformer, but its windings are connected in such a way that it can supply current to both sides of the load.
Types of Distribution Transformer
Since distribution transformers are used for voltage regulation and load distribution, they come in several sizes, rated by voltages and currents. And these can be classified into four types based on their application.
Single Phase
This distribution transformer is designed for single-phase power systems. The primary winding of this transformer is connected to an incoming 3-phase supply line through 3 separate terminals. It has one secondary winding for each phase and is connected to the load through different terminals. The secondary voltage is equal to the sum of all three phases multiplied by their respective turns ratio of the primary windings.
Three Phase
On the other hand, this type of distribution transformer is intended for three-phase power systems. It has three secondary windings connected in a delta connection with a shared neutral wire (ground). Each of these three secondary windings has a different voltage depending on their turn ratio relative to one another. For example, a three-phase transformer with four poles will have three secondary windings with 120 degrees and one voltage winding connected to all three others equally (in parallel).
Pad-Mounted
These transformers are installed directly on concrete pads or pad foundations. It can be used in place of conventional pad-mounted transformers by using a direct burial cable, which allows you to bury power lines underground without worrying about corrosion or breakage.
Typical applications include small commercial buildings, apartment complexes, and industrial plants where the need for more than one phase is minimal or not required (for example, one phase may be used for lighting while another is used for heating). Or it can also be used in areas with no overhead wires, or safety may be an issue due to high voltage lines being present near an electrical substation.
Pole Mounted
These are designed to be mounted on poles above ground level so they can be easily accessed when necessary. They are also used for pole-mounting of special purpose transformer banks such as capacitor or recloser banks. Pole-mounted transformers may have an internal grounding system or an external grounding connection point for use with a separate grounding electrode system. This type of distribution transformer may also include other features such as bushings, lightning arrestors, and surge arrestors.
Difference Between Power Transformer and Distribution Transformer
Power Transformers and Distribution Transformers are used for high voltage, low current applications. However, there are some differences between the two:
Transformer Size / Insulation Level
Power transformers have a higher insulation level than distribution transformers. Power transformers have a voltage rating of more than 1 kV and can withstand short circuit currents up to a few hundred amperes. In comparison, distribution transformers have a voltage rating of less than 1 kV and can withstand short circuit currents up to tens of amperes.
Iron Losses and Copper Losses
Power transformers lose energy as heat due to eddy current losses in their steel laminations and hysteresis losses in the core material. Distribution transformers don’t have any iron parts, so they have lower iron losses than power transformers. They also lose energy due to hysteresis losses in the core material. Still, these are much smaller than power transformers because distribution transformers are smaller, so they don’t generate as much heat as power transformers do when carrying heavy currents.
Maximum Efficiency
Power transformers are generally less efficient than distribution transformers because of their larger size and heavier currents. A typical distribution transformer might have an efficiency rating of 90% or better than 80% for a standard power transformer. However, there are types of power transformers with efficiencies varying from 97 to 99 percent.
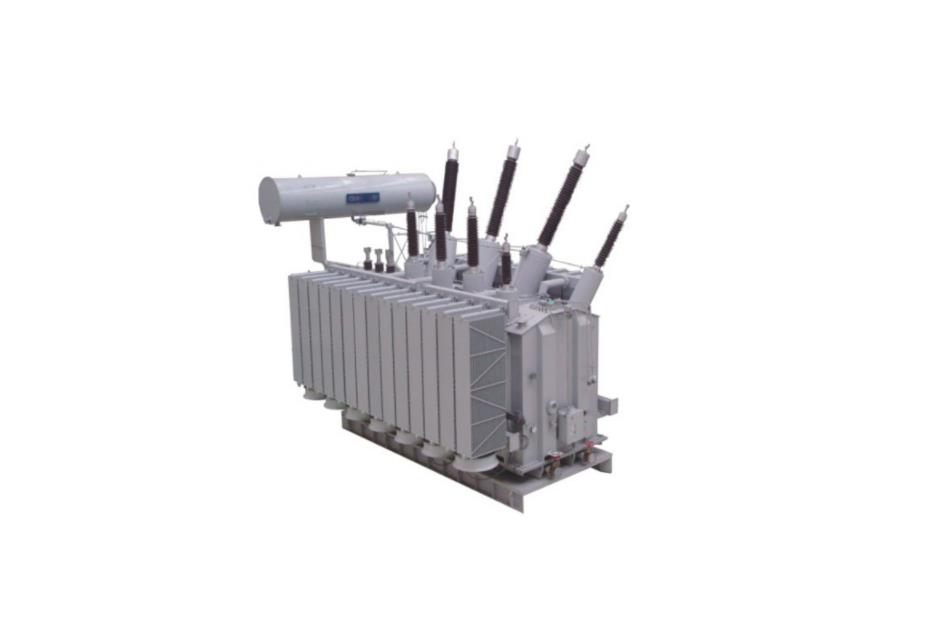
CHINT Power Transformer
When it comes to reliable power transformers, Chint Transformers is your brand. Our transformers are available in different ratings and configurations to meet various applications and industries. Built with quality, safety, and reliability in mind, each product is backed by extensive testing and analysis. Our power transformer line includes:
Distribution Transformer (up to 35kV)
Its features include high security, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance. It also has a long service life because of its high reliability and high-quality materials.
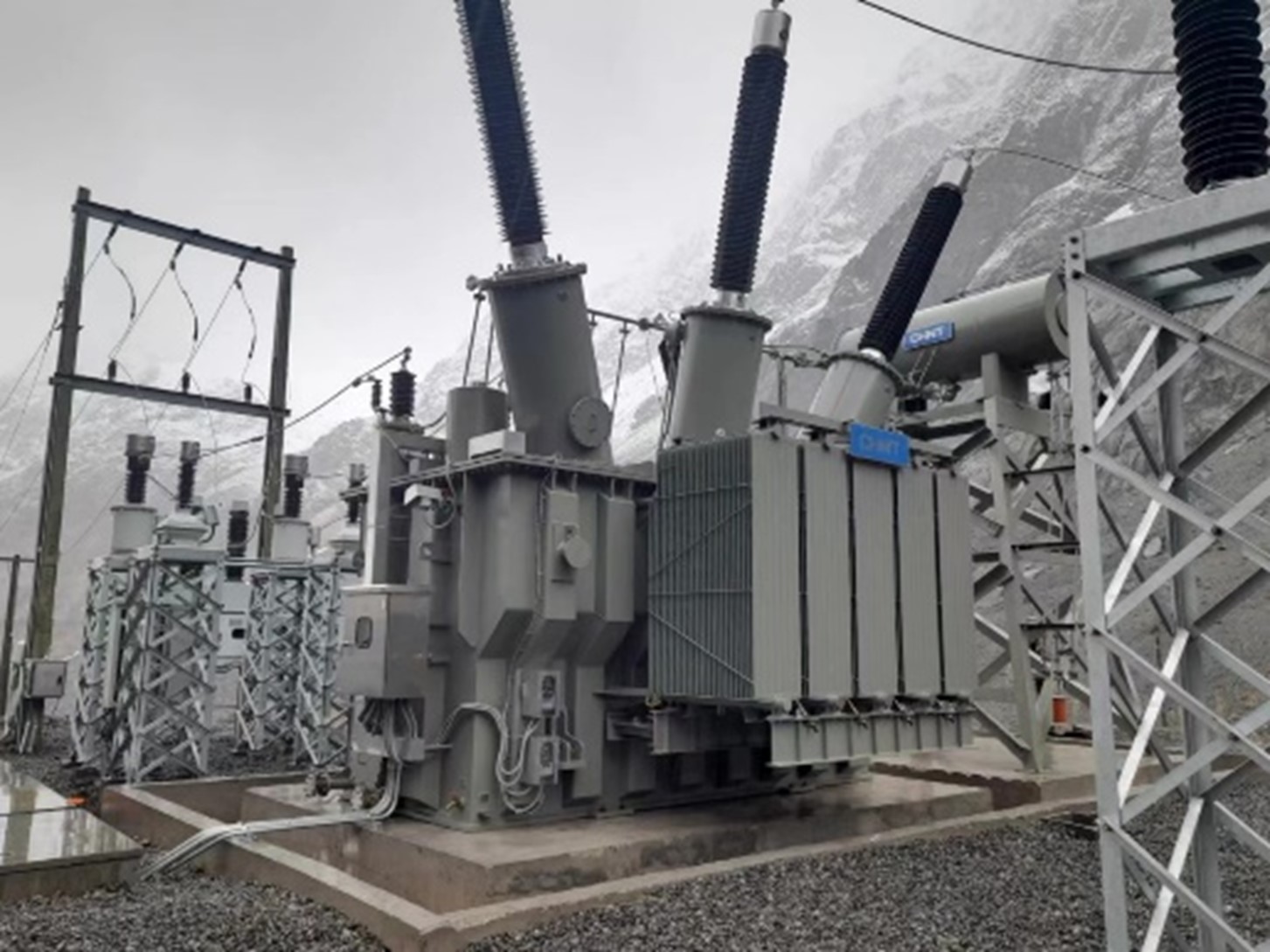
220kV Power Transformer
Its features include low cost per kilowatt, light weight per kilowatt capacity ratio compared with other types of 220kV unit transformers; small volume per kilowatt capacity; simple structure; easy operation and maintenance; low noise level; reliable performance; safe operation performance under partial load condition; and so on.
This transformer is used to convert the voltage between different systems that are in series or parallel connections. The transformer consists of a primary and secondary coil separated by a magnetic core material which allows the transfer of electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction.
Conclusion
While power transformers are designed to step up or down voltage levels for transmission purposes, distribution transformers are made specifically to provide stepped-down voltages to consumers. There are various distribution transformers available on the market, each with its advantages and disadvantages. If you’re looking for a high-quality power transformer to meet your specific needs, we highly recommend trying products from CHINT. With years of experience in the industry, we know how to design and manufacture top-of-the-line transformers that will exceed your expectations.










-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)




