Table of Contents |
A voltage protection relay system is a necessary component of any electrical setup. It prevents safety hazards and damage to equipment. It monitors voltage to determine if levels rise too high or dip too low. Many industries use voltage protection relay systems, especially those in high-voltage situations.
Below, we’ll delve further into how relay systems work, why they’re important, and how you can use them in your electrical setup.
Protective Relay Working Principle
Protective relay systems are part of an electrical circuit. The relay system monitors the voltage of the electricity flow in case the voltage goes above or below a preset standard. If the voltage fluctuates too much, the relay trips, shutting off the system and preventing equipment damage and safety issues.
Relay systems have two main components – a wire with an iron core and a switch. As voltage passes through the wire, it generates an electromagnetic field. If the voltage deviates from the set metrics, the relay wire will trip the system, turning off the electricity. Essentially, it sends a message to the circuit breaker so that it will throw the circuit. After a set time, the relay will allow the current to resume, and the machine can return to normal operations.
Voltage relays are typically more effective than using circuit breakers alone, as a relay is much more sensitive to power fluctuations.
While voltage protection relays primarily work with two-stage AC/DC systems, there are also relays that work with single- and three-phase setups. These relays are designed to detect irregularities.
What is the Main Function of Protection Relays?
Protective relays serve one primary purpose – to trip the circuit in the event of high or low voltage. The relay is a safety feature that prevents serious complications in electrical setups. Protective relays are set up with preset voltage values of minimum and maximum acceptable voltages, unique to each electrical situation. Anything outside of the acceptable range could cause equipment damage or safety hazards.
If the voltage runs too high, it can damage equipment connected to the circuit. Overvoltage can also cause electrical fires and increases the potential for dangerous situations, such as electrocution.
When the voltage runs too low, it can also cause issues. It may damage equipment or prevent processes from running normally. Protective relays can also lengthen the lifespan of expensive equipment, as they keep things running normally.
Types of Voltage Protective Relays
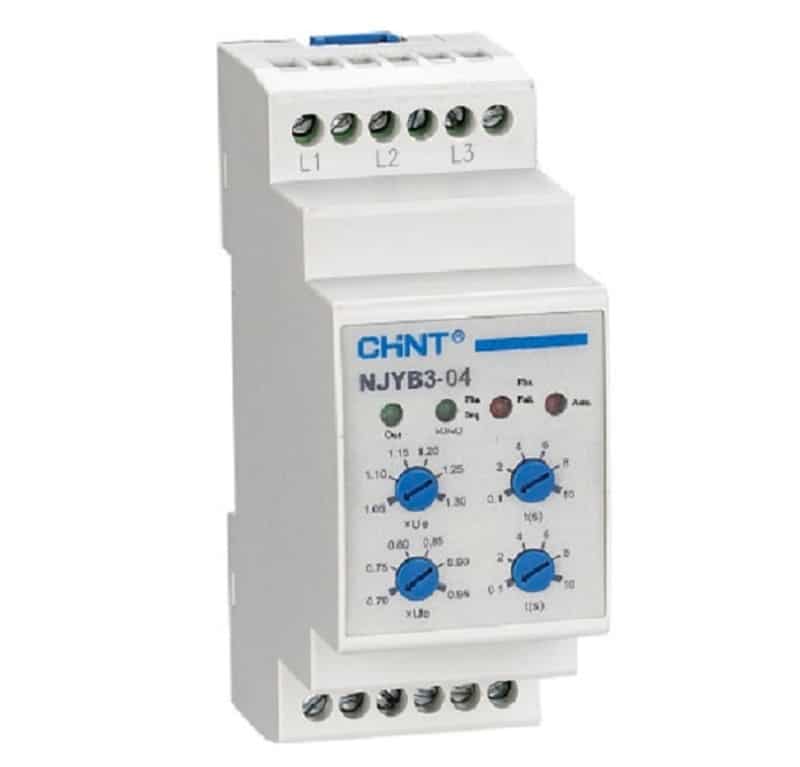
There are several types of voltage relays to fit different situations. There are relays for under voltage and for over voltage. In cases where you need to monitor for both over and under voltage, a few relays on the market can detect both. There are also relays for single-phase and three-phase situations.
Many newer protection relays can determine whether an over or under voltage situation is severe enough for a system shutdown. In some cases, a minor aberration will fix itself and doesn’t require a shut-off. Some will also resume the system after a set time. These relays save time and keep processes running smoothly.
Under Voltage Relays
Under voltage relays, also known as low voltage relays, work by detecting when the electrical current dips under a set value. If voltage dips too quickly, machinery may not have enough power to continue functioning.
An under voltage relay detects when the voltage drops below the preset minimum. When it does, it trips the breaker, opening the circuit and shutting down all equipment connected to the circuit.
Over Voltage Relays
Over voltage protection relays detect when the current’s voltage exceeds a preset value. If the voltage gets too high, the relay will trigger the breaker. The entire system will shut down. Systems involving the transfer of electricity often use over voltage relays to prevent equipment damage.
Application of Voltage Protective Relays
Many industries use protective relays, particularly those running a lot of machinery and those in areas that are prone to lightning strikes. Even smaller home appliances often have voltage relays.
One example of a voltage protection relay where overvoltage is a concern would be in a power plant. Electrical currents flow to transformers, but an overload could damage the transformers. A relay can monitor the current, and if it senses a consistent overlead issue, it can shut off the current, protecting the transformers.
For an under-voltage situation, consider a manufacturing plant. If the current to a motor dips below the rated value, it could force the motor to work abnormally. This could cause problems with the production process and damage the engine, potentially burning it out.
Installation and Maintenance of Voltage Protective Relays
When installing voltage protective relays, you’ll work with electricity in a potentially dangerous situation. If you are not a trained electrician, it’s best to hire a professional to help. They will ensure a safe installation and a product that works properly.
It’s also important that the protective relay undergoes regular maintenance. You, or a qualified electrician, should go through the device, making sure all parts are in good working order and that all parts make good connections.
You’ll also want to perform a series of tests to ensure the relay works properly. Be sure to perform an end-to-end test along with tests at each connection to isolate any issues.
Conclusion
Voltage protection relays are an essential component of many electrical setups, especially where dips and spikes in current voltage can cause equipment damage and present safety threats.
Chint Global offers a variety of protective relays, including the NJYB2 Series, a relay designed for AC frequency at 50Hz. Our representatives are ready to help you find the best product for your situation. Contact us today to learn more.
FAQ about Voltage Protection Relay
Why is a Voltage Protection Relay necessary?
What are the key features to look for in a Voltage Protection Relay?
Can a Voltage Protection Relay be used in any type of electrical system?