Table of Contents |
Converting a low electrical input into something like a high-current output is not a simple process. Still, it is essential to effectively run various basic appliances and machines, including cars and trucks. Some circuits accomplish these conversions by using relays, which are necessary components in almost all types of electronic machinery.
Most of you probably know about this tool, but some of you are still new to the concept, so in this article, I will guide you on everything you need to know about relays, different types of relays, and how a relay works and most importantly, why you need to install it.
What Is a Relay? and how does it work?
A relay is an electrical converter that transforms minor electrical inputs into higher currents using electromagnetism. This kind of transition occurs whenever electrical inputs cause electromagnets to establish or change old circuits due to the electrical information.
Depending on the application, relays serve as either a converter or a booster for electrical circuits.
What is a Protection Relay?
The switchgear may detect each malfunction inside the power circuit. The relay may trigger the circuit breaker, disconnecting any malfunctioning components inside the system. A protective relay must be installed in the power system to maintain and regulate every unexpected circuit circumstance.
It can determine the electrical component of a circuit and determine if it is operating under normal or strange circumstances. An electric system’s frequency, amplitude, current, and resistance are only a few elements that protective relays can regulate.
Once a variable’s reading signals an abnormal behavior, a warning indicating a defect is transmitted to the protective relays, together with the location and kind of the problem.
Once the problem is detected, the breaker’s trip circuit will be immediately shut by a protective relay by disconnecting the circuits with issues.
What are the different types of Protective Relay?
Protection relays are available in a range of designs and sizes. The following are by far the most essential and often used kinds of protective relays:
Electromagnetic Relays
Electromagnetic relays were the first relays invented and are still used in several locations presently. In electromagnetic operated relays, the operational current passes through the primary coil.
Once the current flow rises, the coil stimulates the electromagnet, raising the voltage level. Because of the strong magnetic field created by the electromagnet as the running current increases, this magnetism pulls the shaft or pusher, which causes the trip circuit connections to shut.
Static Relays
The electromagnetic relay may be transformed into a static relay, and the electromagnetic relays receive the characteristics of the working component from the static relay through an electrical system.
For instance, the disc regulates the operation period of an induced relay by adjusting the distance. Furthermore, the R-C time (tau, or R-C circuit) delay of a static relay is adjusted by altering the circuit’s resistivity.
In other words, the static relay’s circuitry controller owns the operations handled by the active component inside the electromagnetic relay.
Digital / Numerical Relays
Electrical (analog) volumes are collected and turned into numbers or digital data, which will then be managed analytically. A comprehensive analysis is taken about whether or not to trip the switch.
Numerical/digital relays use a specialized analog to digital converter or digital signal processor (DSP) and other utility programs to do the tasks that make them work. The relaying output and current flow go through a generator to keep them under control.
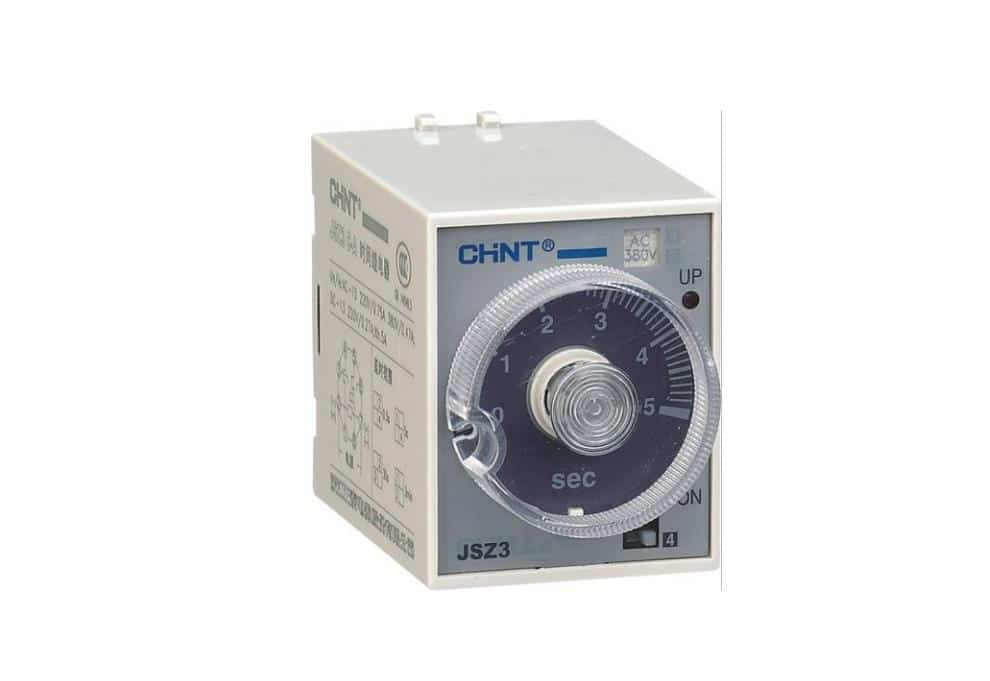
What is a Time relay?
An electromagnet is utilized in order to regulate the electric flow in a circuit. A time relay is an electronic component that does this. The coil of wire is rolled up around an iron core. Once the electricity goes through the loop, it makes a magnetization in the electromagnets.
A magnet connected to a timed relay circuit within the gadget may be attracted or repelled by this magnetism. You can regulate whenever this occurs by adjusting how quickly the electricity travels thru the time relay’s circuits before it stops.
On delay timer relay
The output link moves whenever the supply power increases and the delay period is already over. Once the supply voltage drops below a certain level (when one fan begins to run), the output link returns to the initial position. (And the fan shuts down.)
Off delay timer relay
Once the voltage level is delivered, the off-delay circuits are prepared to receive the trigger and begin working. Putting the trigger activates outputs, which must then be deleted in order again for the time delay to start. The de-energization of output occurs after the time delay duration. If such a trigger is delivered during the delay, this will cause the delay to be restarted.
Multifunction timer relay
A multipurpose time relay is a device that can perform various timed tasks. A multifunctional timer may be used to choose and apply several regulating actions. It’s ideal for a wide range of operations, from simple to complex controllers.
What is a General Purpose Relay?
General purpose relays are primarily utilized as a control system (relay series) for automated equipment at different manufacturing locations and different construction process control like lights, air conditioners, and water management.
CHINT Relay
The CHINT relay collection offers many sets and powerful features, allowing it to be used in a wide range of applications, including everyday consumer electronics, industrial automation circuitry, and mechanical components. Here are the following:
JD-8 Integrated Motor Protector
The JD-8 Integrated Motor Protector is primarily used to prevent minimal three-phase AC asynchronous motors against heavy load and phases breakdown in power systems utilizing AC frequencies and minimum insulator voltages. In an Armature loop circuit, the defender is usually paired with a relay for usage.
KG10D Time Switch
The KG10D Time Switch will immediately turn on or off the electrical supply to a range of consumer electronics based on a user-defined timeframe. Controlled devices include circuit gear and home appliances like street lighting, fluorescent lamps, commercial lighting, industrial equipment, telecommunication & broadcasting tools, and others that need on-and-off operation at designated times.
JQX-13F Miniature High-Power Electromagnetic Relay
With a contact switching capacity of 10A, JQX-13F Miniature High-Power Electromagnetic Relay is a comprehensive spectrum of AC/DC requirements integrated with a clear dust cover, several installation options, and a wide selection of connectors. This device is ideal for many applications.
Conclusion
A malfunction or undesired fluctuation in components such as currents and voltages may cause electrical system failure and other disastrous complications. Even if a relay isn’t required, utilizing one might be helpful for you. Relays can replace high-amperage cables and controls, saving money and space.









.png)





