From January to May 2020, the scale of China’s PV module exports reached 26.2GW, down 2.82GW from 29.02GW in the same period of the previous year, narrowing the decline to 10.76%. The impact of the epidemic on overseas markets mainly occurred in the second quarter, the overseas epidemic led to the post ponement of market demand in South America, India, France and other overseas markets.
And China is the world’s largest producer of photovoltaic products and the main demand for photovoltaic products comes from overseas markets. The decline in installation capacity in overseas markets has a certain impact on the domestic photovoltaic manufacturing industry, and the overseas market layout of photovoltaic enterprises has slowed down.
The impact of the epidemic on small manufacturers is much greater than the leading manufacturers, which in turn has caused many small manufacturers using the old capacity to shut down or withdraw, will further enhance the concentration of the industry.
As the price of photovoltaic products continue to fall and the cost of power generation continues to reduce, photovoltaic power generation in more and more countries are widely used, due to the dynamics of the global epidemic and the economic restart process indifferent countries, the trend of polarization of overseas PV demand gradually emerged, the global PV export market will also be further fragmented.
Positive Changes Emerged In Total Number & Structures of Overseas Markets
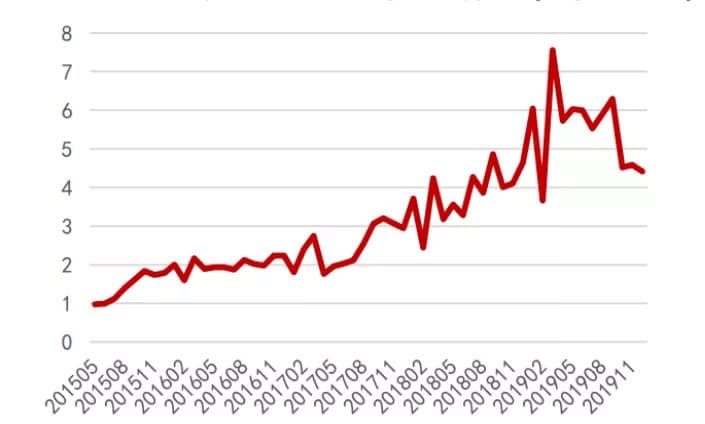
From the perspective of export data, exports have shown an accelerating trend since the second half of 2017, and the component export data from 2014 to 2016 were more volatile, but since 2017, there has been a significant growth in component exports, and due to the big drop in industry chain prices in 2018, which stimulated overseas demand, 39.2GW of component exports were realized in 2018, up 51.9% year-on-year, and component exports total volume in 2019 is 66.3GW, up 43.5% year-on-year.
The export scale of PV modules has grown rapidly since 2017(Unit:GW)
The Concentration of Photovoltaic Module Export Market Continues To Decrease
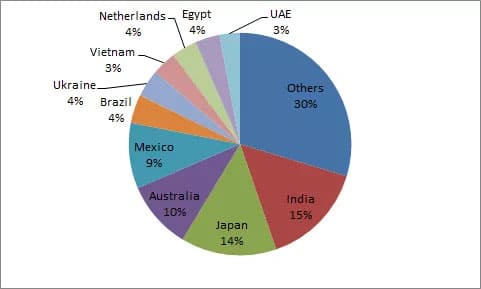
CR5 was 67.1% in 2017, 53% in 2018, and 36.3% in 2019, indicating that emerging countries with PV installations are on the rise, and global installations are showing a multi-point blossoming situation. Reduced concentration will reduce the dependence of the industry chain on a single market, more conducive to the healthy development of the market.
Exports of 12.99 billion U.S. dollars in 2018
Multi-Point Bloom in Overseas Markets
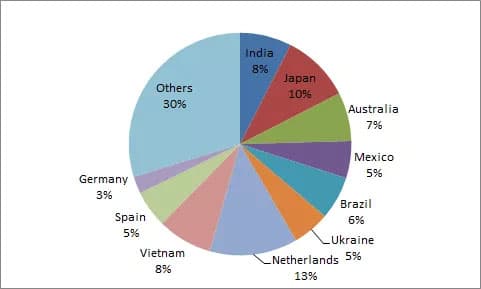
Total PV module exports from January to December 2019 were 57.3GW, up 53.0% year-on-year, with the Netherlands, Vietnam, Spain, Brazil, Ukraine, Germany, Portugal and Japan growing at a higher rate and year-on-year. The rapidly declining cost of photovoltaic energy is highlighting its strong economics in more and more countries.
Exports of 17.31 billion U.S. dollars in 2019
Export Products Under The Strengthened Epidemic Quarantine
The epidemic will lead to the strengthening of export product quarantine, or to short-term foreign trade of photovoltaic products setback. But in the medium and long term, the overseas market parity area to further expand, installation demand will continue to be strong, and overseas power stations and domestic manufacturers mostly signed long-order agreement, short-term product export quarantine on the delivery schedule or moved back, but does not affect the market demand in the medium and long term.
From the perspective of the global PV industry chain, China has firmly occupied the leading position in the PV industry chain. Data released by the China Photovoltaic Industry Association shows that as of 2019, China has ranked first in the world in terms of new installations for seven consecutive years, first in cumulative installations for five consecutive years, first in poly silicon production for nine consecutive years, and first in module production for 13 consecutive years. 2019, China’s share of silicon, wafers, cells, and modules in global production was 67%, 98%, 83%, and 77%, respectively. The production of each segment continues to steadily increase.
Meanwhile, overseas silicon giants are in business difficulties and local substitution is expected to accelerate. WACKER and OCI are two of the largest overseas silicon companies, and the profitability of the polysilicon business of both companies showed a significant decline in 2019 amid a significant year-on-year decline in silicon prices.
Overall, the technology and product quality gap between domestic silicon companies and overseas giants continues to narrow, with obvious cost advantages. Under the impact of large-scale, low-cost silicon capacity, polysilicon prices continued to decline in 2019 despite the faster growth of new PV installations worldwide.
Due to the increase in the proportion of monocrystalline on the demand side, the price decline of dense material is significantly smaller compared to sparse material. After OCI clearly minimizes the production of solar-grade polysiliconat its base in South Korea, it is expected that the proportion of imported silicon in China will be further reduced in the future.
In the future, high efficiency and reliability are not the only indicators of PV products. The requirements of intelligence, lightweight, and integration with buildings will make the products more diversified and suitable for a variety of applications and installation conditions. Automation, intelligence, flexibility of PV manufacturing and the future global virtual factory are the main trends of the current industrial upgrade.
As the product technology and manufacturing process continue to advance, PV manufacturing will be more similar to the precision manufacturing of semiconductors, and the degree of product integration will continue to increase.