Table of Contents |
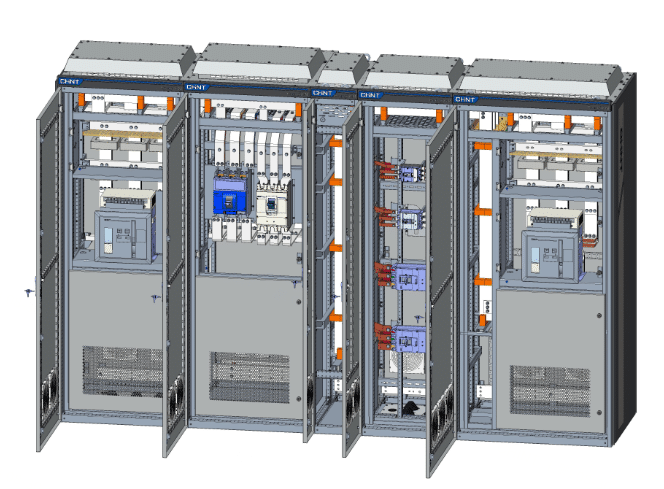
LV distribution boards, part of the electrical distribution system, securely distribute low-voltage power to facility circuits. Integrated with ACBs and MCCBs, they provide protection from overloads, short circuits, and others. They also centralize power distribution monitoring and management for repair and diagnostics. Read on to gain a comprehensive understanding of LV distribution boards.
Types of LV Distribution Boards
LV distribution boards can generally be categorized into 3 types:
Main Distribution Board
Main distribution boards (MDB) manage and distribute electrical power from one or more sources to branch circuits in an LV distribution system. It provides circuit breakers for each branch circuit to prevent faults and incidents. Further, its architecture allows future expansions on circuits without major reconfiguration.
Sub-Main Distribution Board
Sub-main distribution boards (SMDB) distribute electricity from the MDB to specified zones or locations. Sectioning the electrical supply for easy management and improved safety is the main purpose of sub-main distribution boards. An SMDB might serve a big complex’s HVAC systems or lighting circuits.
Final Distribution Box
As the name indicates, the final distribution box (FDB) supplies power to end-user devices and appliances. It is an essential device for safe and easy power access at the use point. FDBs might feature miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) or residual current devices (RCDs) to guard against overcurrents and electric shock. In domestic settings, an FDB may feed individual rooms or equipment like water heaters or ovens. It adapts electrical distribution to exact demand profiles.
Common Applications of LV Distribution Boards
LV distribution boards are often found in power utilities, high-rise buildings, industrial settings, data centers, and new energy plants.
Power Utility
LV distribution boards allow power utilities to distribute and control low-voltage energy in residential and business areas. Substation auxiliary systems use these boards to control room equipment, lighting, and other services.
Buildings
Electrical security and effectiveness in buildings depend on the integration of the LV distribution boards. They centralize electrical distribution for precise control over lighting circuits, HVAC systems, and elevators. They also provide overload and short circuit protection to prevent electrical fires and assure system integrity.
Industrial OEM
LV distribution boards are important for OEM machinery and equipment design and operation. They secure and organize power distribution to motors, control units, and sensing devices in industrial equipment. Apart from that, these boards also defend against dust, moisture, and mechanical impacts in rugged industrial settings. Steady and dependable equipment operation can be assured.
Data Center
LV distribution boards provide stable electricity to IT equipment and cooling systems in data centers. They can interact with UPS systems and backup generators. Data centers can monitor and regulate power distribution using these boards for optimal energy usage and performance.
New Energy
The new energy industry uses LV distribution boards to distribute electricity from renewable sources (solar panels and wind turbines). The grid’s integration of renewable energy, power flow management, and stability depend on these boards. They help energy storage systems reconcile supply and demand and convert DC to AC power when needed.
Common Components of an LV Distribution Board
ACB (Air Circuit Breaker): ACBs are used in LV distribution boards for high-current interruption to safeguard and optimize electrical systems. These devices provide accurate short-circuit and overload protection with customizable trip settings.
MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker): LV distribution boards also incorporate MCCBs on the load side to guard against overload and short-circuit. Its small size renders it easier to integrate into other systems. MCCBs feature thermal-magnetic or electronic trip units and can be customized to provide different protective schemes for specific energy needs.
Conclusion
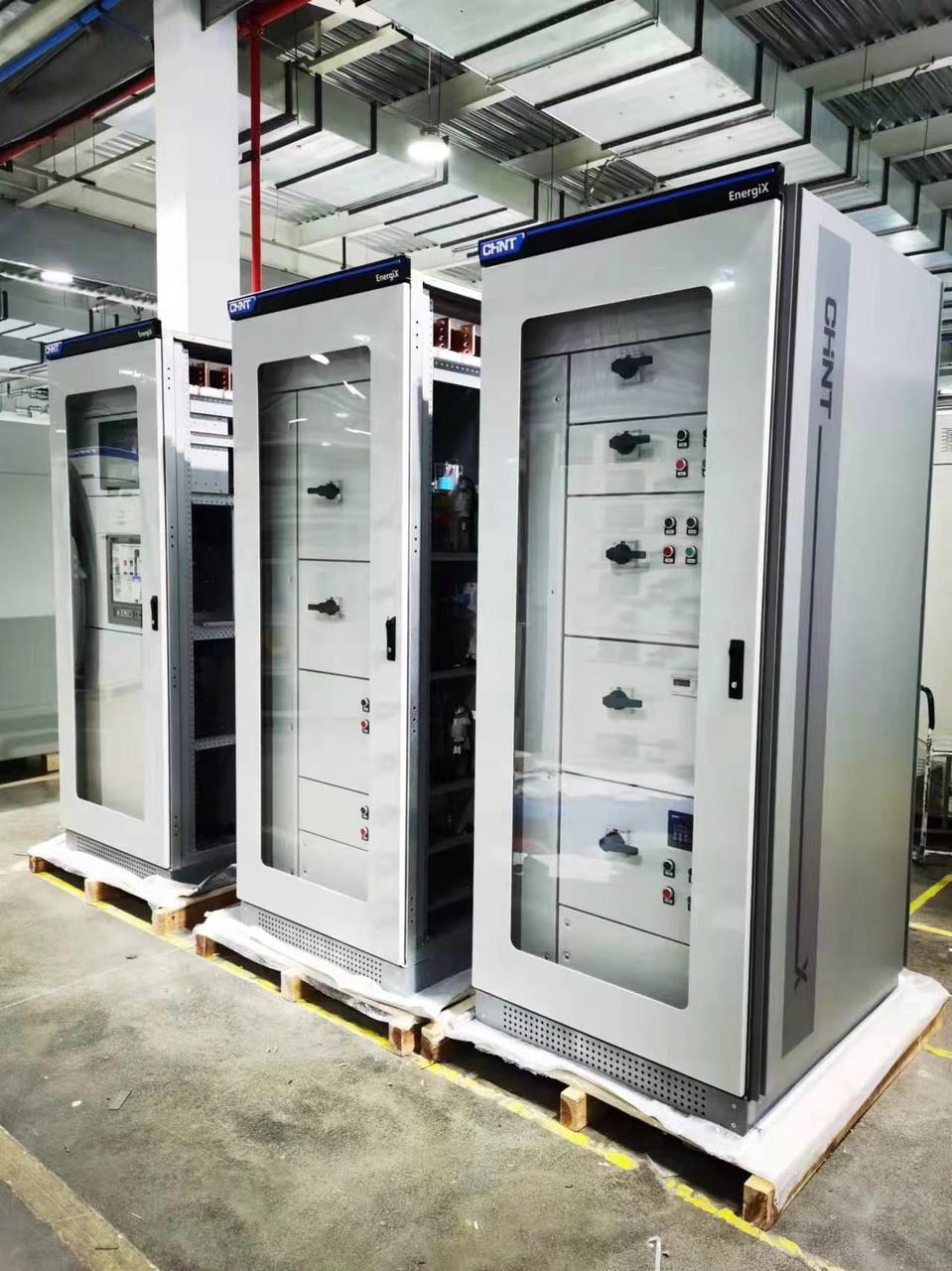
Overall, LV distribution boards form the backbone of electrical distribution systems. They ensure reliable power distribution for a wide range of settings. For those who want to invest in LV distribution boards, CHINT’s brand new TTA EnergiX series switchgear stands out as a reliable option.
As the exclusive authorized cooperation product, EnergiX plays a significant role in CHINT localization and cooperation with local panel builder partners. Thanks to its IP54 dust and water protection certification, the TTA EnergiX-M performs well at 50℃ ambient temperature, suitable for some hot areas. Its antimagnetic construction avoids eddy current losses. Its communication channel design protects control signals in complex electrical systems from electromagnetic interference. Visit the website to discover more about EnergiX-M and other devices.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to us.












-metalclad-AC-enclosed-switchgear-banner.png)




